Introducing the Alphabet of Genetics: Understanding Codons
In the realms of biology, the intricate mechanisms of life’s blueprints lie hidden within a microscopic world called the genome. DNA, the cornerstone of genetic inheritance, comprises sequences of nucleotides arranged in a specific language, much like the words and sentences that convey meaning in the human tongue. The fundamental building blocks of this genetic language are known as codons, a series of three nucleotides that play a pivotal role in translating the genetic code into the proteins responsible for life’s numerous processes.
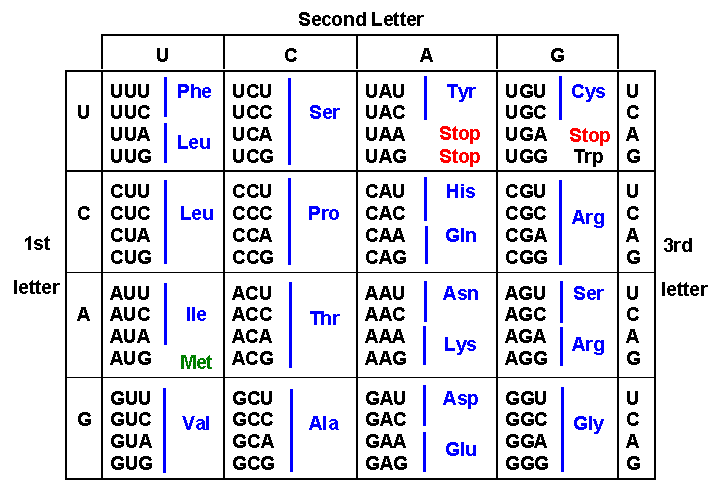
Image: facweb.furman.edu
As the blueprint of every living organism, DNA encodes the instructions necessary for cell development, function, and reproduction. Within its structure, DNA harbors genes, specific regions that act as the templates for creating proteins, the workhorses of cells. To bridge the gap between the DNA blueprint and the resultant proteins, cells employ a sophisticated decoding mechanism that relies on codons.
The ABCs of Codons: A Genetic Vocabulary Decoder
Each codon consists of a trio of nucleotides, the molecular subunits of DNA—adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These nucleotides form the genetic alphabet, similar to the 26 letters that make up the English language. The combination of codons specifies which amino acid will be added to a growing protein chain during protein synthesis, the process by which DNA’s instructions are translated into functional entities within the cell.
Imagine codons as specific words within the genetic code, each encoding a distinct amino acid, the elemental units of proteins. For instance, the codon ‘AUG’ corresponds to the amino acid methionine, which often serves as the starting point for protein synthesis. Similarly, the codon ‘UAA’ acts as a stop signal, indicating the end of protein production.
The Translator Powerhouse: Ribosomes at the Protein Factory
Ribosomes, the cellular machines responsible for protein synthesis, act as the interpreters of the genetic code, translating the codon sequences into the linguistic tapestry of proteins. During translation, the ribosome ‘reads’ the sequence of codons on messenger RNA (mRNA), the intermediary molecule that carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
Each codon on mRNA binds to a specific transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule carrying the corresponding amino acid. The ribosome then catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids, linking them together in a linear chain that eventually folds into a protein with a unique three-dimensional structure and distinct functionalities.
Cracking the code: The Science of Genomics
Understanding codons has unlocked a wealth of knowledge in the burgeoning field of genomics, the study of genomes. Genomics has advanced medical research by allowing the identification of genetic variations linked to diseases, unraveling the mysteries of genetic inheritance, and tailoring treatments based on a person’s specific genetic makeup.
Moreover, codons have become essential tools in biotechnology, enabling scientists to synthesize specific proteins for a wide range of applications, spanning from medical diagnostics to industrial processes. By manipulating codons in genetically modified organisms, scientists can engineer proteins with novel properties and enhance their therapeutic potential.
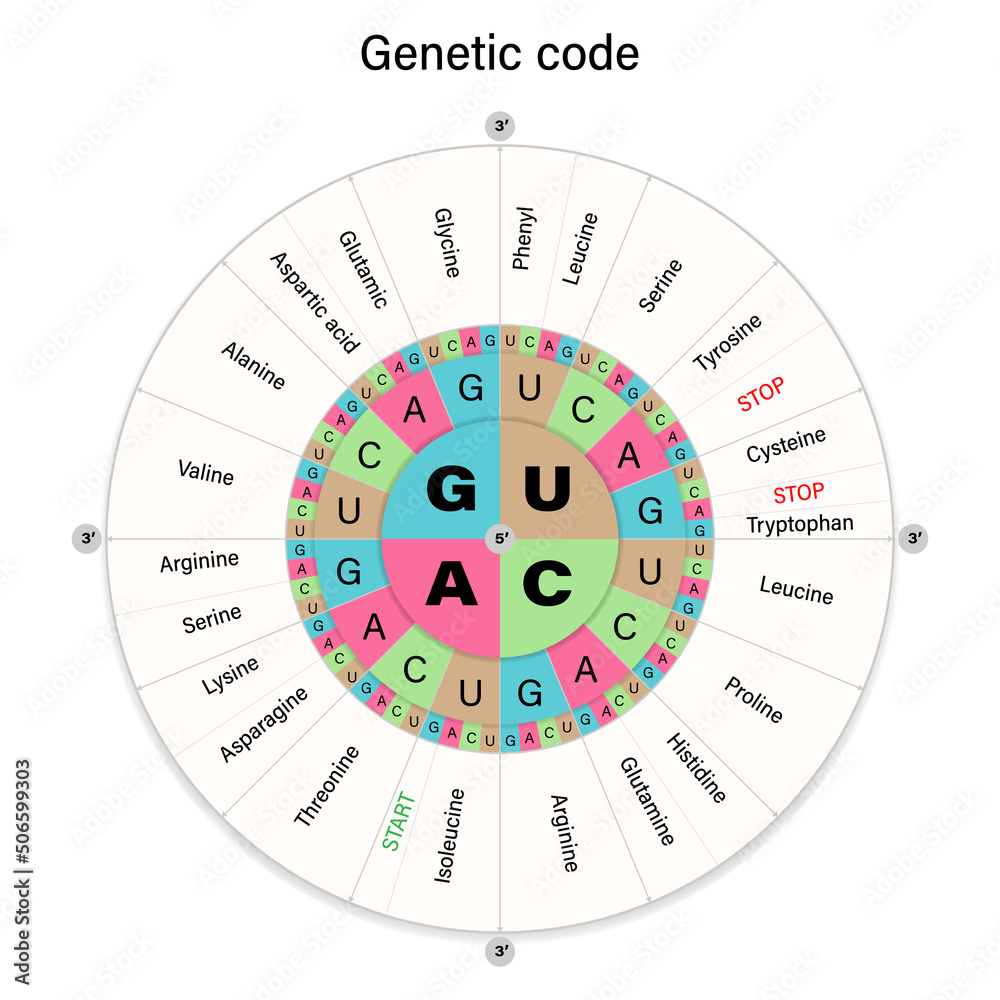
Image: stock.adobe.com
A Codon Is A Sequence Of Three Bases On
Conclusion: The Essence of Life
In the symphony of life, codons are the silent conductors,orchestrating the production of proteins that govern our every action, thought, and physiological process. As we delve deeper into the exquisite chemistry of life,deciphering the language of codons will pave the way for unprecedented advancements in medicine and technology, illuminating the path towards personalised treatments, disease prevention, and a better understanding of the very essence of life itself.